Array
Array is one of the most foundamental data structure in computer science. I think this would be the first structure you learn in your cs courses. However, it is very important and it teaches a lot of basic principles you will encounter in the future.
First, what is Array?
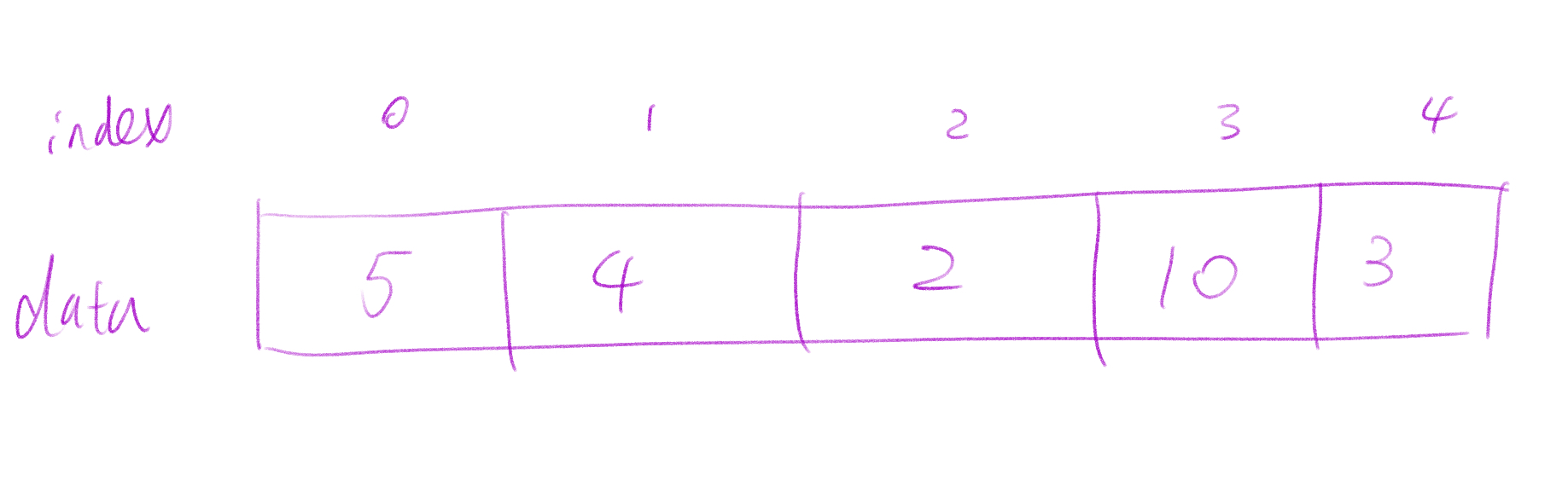
An array in C++ is a series of elements of the same type placed in contiguous memory locations that can be individually referenced by adding an index to a unique identifier.
Note that although we use C++ and Java in most of the examples in data structure and algo section , the language doesnt matter and we wont cover any language tutorial on the website. There are many great website for your to explore different programming languages. Dont worry about that. In your interviews, you are likely to be allowed choose whatever language you feel comfortble with.
There are two main charaters which need your attention: same type and contiguous memory locations.
First feature is more useful when we are talking about inheritance and polymorphism. contiguous memory locations is what we focus in DSA. Thanks to this feature, we could access items with an index in constant time (i.e. O(1) if we use asymtopic notation).
Please note that there is no plan to have a Big-O tutorial for now. This topic is usually prerequisite of DSA courses. Again, there are many resources out there. Feel free to google it or learn it with ChatGPT lol.
However, this feature also brings many problems. One of the most popular problem is memory utilization. If you have learned operating system, you may know that our memory is segmented by many programs. Therefore, finding a large contiguous is very costly and could not utilize memory really efficient.
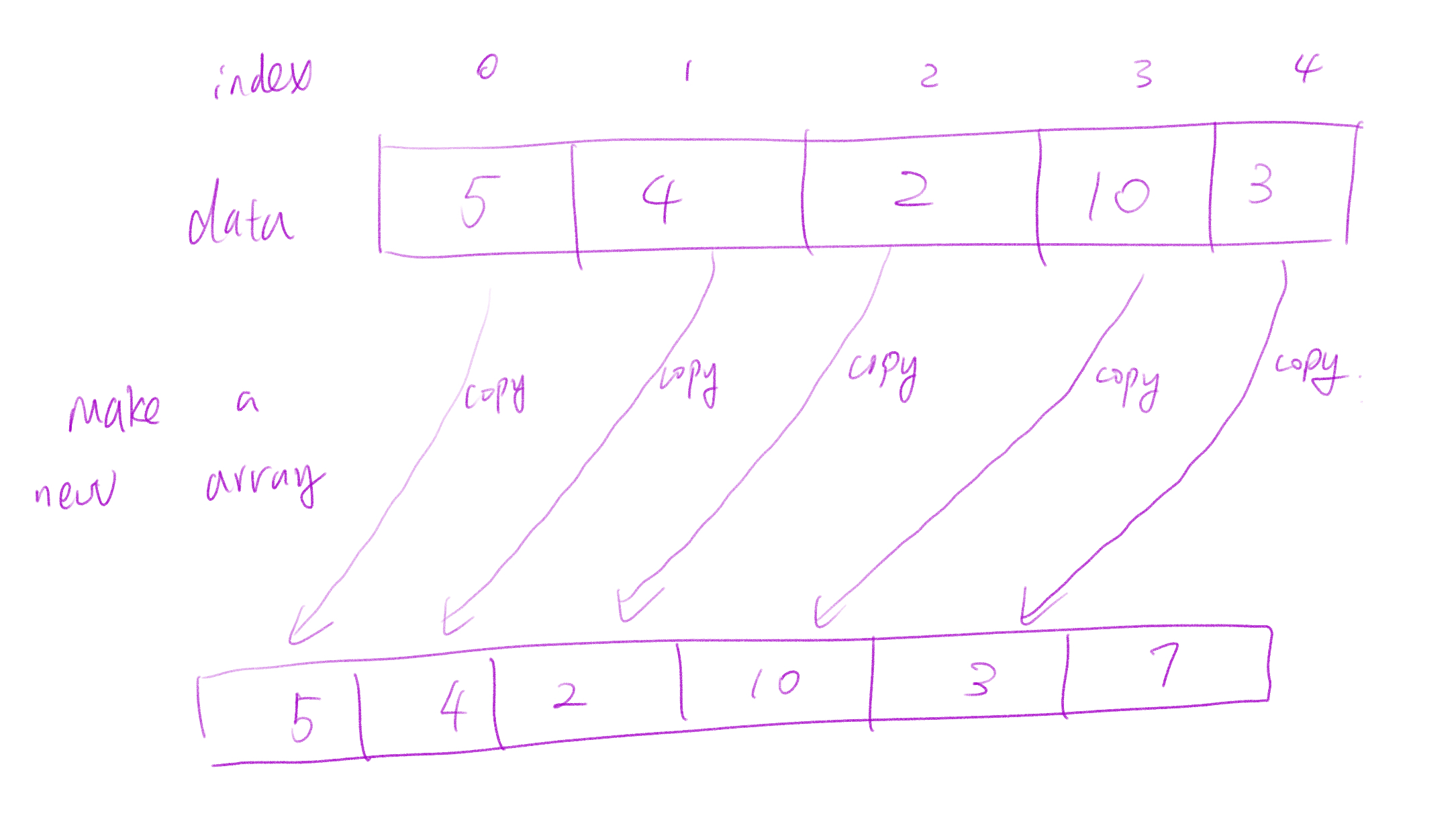
Another problem is the size of array is fixed. For example, if you have an array with 6 blocks, then you can only store 6 elements in this array. However, if you would like to fit more elements, there is no easy way to do that. You can only create a new array with a larger size and move all elements from the old array to the new array. The runtime complexity of this operation would be O(n), we also call it linear complexity.